Chinese
Medicine

It is our pleasure, purpose, and goal to share Connection - Holistic Lifestyle - Alternative Healing Treatments - Living Happier with New Thought - from original sources.
GlobalCnet is a collection of links to original thought, research, new ideas, and found expert advice.
We have assembled extensive information and facts to inspire YOU to further your education, skills, and desires on your specific subjects.
When you click on a blue link, you arrive at a website, do your research, and observe all the other articles available to you.
Record what you need.
Share what you learned.
GlobalCnet connected you, to make better-informed decisions.
This is a teaching and informative Web Site again, presenting original authors, like Harvard University, MedNet, Unstuck.com, Readers Digest, Mental Health, and documents from millions of Web Sites that were written, published, and illustrated with specific content to expand your knowledge for personal growth, health and answers.
All this WWW content was meant for your reading and answers,
GlobalCnet just connected you.
It is our hope that you use all information for further answerers, ideas for more exploration, and the wisdom to share discoveries with others. It is all about having the right fast or safe connections. Everything has already been discovered, be smart and use proven methods and spin your solutions to fit your needs.
Any questions, comments or to just say hello...leave webmail.
Quick links to information and new ideas. click here.
OK...you are now on GlobalCnet. You can use the SEARCH BAR to quickly find subject information, or you can visit all the pages. Your visit will award an organized starting point leading to answers to your challenge.......just do it. Type in a word and hit search.
- Michael J. Malette, PhD
Founder, Global Connection Network, Inc.
What is Chinese medicine?
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is thousands of years old and has changed little over the centuries.
Its basic concept is that a vital force of life, called Qi, surges through the body.
Any imbalance to Qi can cause disease and illness.
This imbalance is most commonly thought to be caused by an alteration in the opposite and complementary forces that make up the Qi.
These are called yin and yang.
Ancient Chinese believed that humans are microcosms of the larger surrounding universe, and are interconnected with nature and subject to its forces.
A balance between health and disease is a key concept.
TCM treatment seeks to restore this balance through treatment specific to the individual.
It is believed that to regain balance, you must achieve the balance between the internal body organs and the external elements of earth, fire, water, wood, and metal.
Treatment to regain balance may involve:
-
Acupuncture
-
Moxibustion (the burning of herbal leaves on or near the body)
-
Cupping (the use of warmed glass jars to create suction on certain points of the body)
-
Massage
-
Herbal remedies
-
Movement and concentration exercises (such as tai chi)
Acupuncture is a component of TCM commonly found in Western medicine and has received the most study of all the alternative therapies.
Some herbal treatments used in TCM can act as medicines and be very effective but may also have serious side effects.
In 2004, for example, the FDA banned the sale of dietary supplements containing ephedra and plants containing ephedra group alkaloids due to complications, such as heart attack and stroke.
Ephedra is a Chinese herb used in dietary supplements for weight loss and performance enhancement.
However, the ban does not apply to certain herbal products prepared under TCM guidelines intended only for short-term use rather than long-term dosing.
It also does not apply to OTC and prescription drugs or to herbal teas.
If you are thinking of using TCM, a certified practitioner is your safest choice.
The federally recognized Accreditation Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine (ACAOM) accredits schools that teach acupuncture and TCM.
Many of the states that license acupuncture require graduation from an ACAOM-accredited school. The National Certification Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine offers separate certification programs in acupuncture, Chinese herbology, and Oriental bodywork.
TCM should not be used as a replacement for conventional or allopathic treatment, especially for serious conditions, but it may be beneficial when used as a complementary therapy.
Since some TCM herbal medicines can interfere or be toxic when combined with Western medicines, you should inform your doctor if you are using TCM.
Traditional Chinese Medicine: What You Need To Know
 What’s the Bottom Line?
What’s the Bottom Line?
How Much Do We Know About Traditional Chinese Medicine?
The approaches that make up traditional Chinese medicine (such as acupuncture, tai chi, and herbal products) have been the subjects of many clinical studies and scientific reviews.
What Do We Know About the Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine?
Some psychological and/or physical approaches used in traditional Chinese medicine practices, such as acupuncture and tai chi, may help improve quality of life and certain pain conditions. Studies of Chinese herbal products used in traditional Chinese medicine for a range of medical conditions have had mixed results.
What Do We Know About the Safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine?
Some Chinese herbal products have been contaminated with toxic compounds, heavy metals, pesticides, and microorganisms and may have serious side effects. Manufacturing errors, in which one herb is mistakenly replaced with another, also have resulted in serious complications.
What Is Traditional Chinese Medicine?
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has evolved over thousands of years. TCM practitioners use various psychological and/or physical approaches (such as acupuncture and tai chi) as well as herbal products to address health problems.
What the Science Says About the Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine
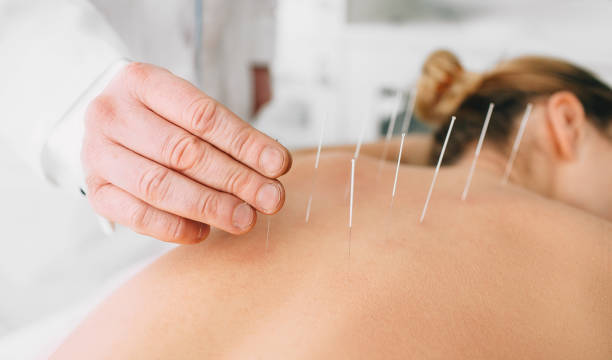
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a technique in which practitioners stimulate specific points on the body, usually by inserting thin needles through the skin.
Studies suggest that acupuncture stimulates the release of the body’s natural painkillers and affects areas in the brain involved in processing pain; however, some trials suggest that real acupuncture and sham acupuncture are equally effective, indicating a placebo effect.
Results from a number of studies, however, suggest real acupuncture may help ease types of pain that are often chronic, such as low-back pain, neck pain, osteoarthritis/knee pain, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
It also may help reduce the frequency of tension headaches and prevent migraine headaches.
For more information, see NCCIH’s acupuncture fact sheet.
Tai Chi
Tai chi combines certain postures, gentle movements, mental focus, breathing, and relaxation. Research findings suggest that practicing tai chi may improve balance and stability in older people and those with Parkinson’s disease, reduce pain from knee osteoarthritis, help people cope with fibromyalgia and back pain, and promote quality of life and improve mood in people with heart failure.
For more information, see NCCIH’s tai chi fact sheet.
Chinese Herbal Products
Chinese herbal products have been studied for many medical problems, including stroke, heart disease, mental disorders, and respiratory diseases (such as bronchitis and the common cold), and a national survey showed that about one in five Americans use them.
Because many studies have been of poor quality, no firm conclusions can be made about their effectiveness.
For more information about specific herbs, see NCCIH’s Herbs at a Glance webpage. You can find additional information on botanical (plant) dietary supplements on the Office of Dietary Supplements website.
What the Science Says About the Safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Reports and studies of herbal products used in TCM have found a variety of safety issues.
- Some Chinese herbal products have been found to be contaminated with undeclared plant or animal material; drugs (such as the blood-thinner warfarin and the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent diclofenac); heavy metals (such as arsenic, lead, and cadmium); pesticides or compounds called sulfites, which could cause asthma or severe allergic reactions; or incorrect herbs, some of which have caused organ damage.
- Relatively few complications from using acupuncture have been reported. Still, complications have resulted from the use of nonsterile needles and improper delivery of treatments. When not delivered properly, acupuncture can cause serious adverse effects, including infections, punctured organs, collapsed lungs, and injury to the central nervous system.
- Tai chi and a similar technique called qigong appear to be safe practices. While it’s unlikely that tai chi will result in serious injury, it may be associated with minor aches and pains. Women who are pregnant should talk with their health care providers before beginning tai chi, qigong, or any other exercise program.
NCCIH-Funded Research
NCCIH is supporting studies to determine if:
- TCM can treat fibromyalgia.
- Acupuncture can ease joint pain caused by medical treatments for breast cancer.
- A tai chi program can be a feasible alternative to traditional cardiac rehabilitation programs in selected people.
More To Consider
- If you’re considering TCM, be sure to discuss this with your health care providers. Don’t use TCM to replace or delay seeking conventional care.
- If you have a health condition, talk with your health care provider before using TCM herbal products.
- Ask about the training and experience of the TCM practitioner you are considering. Most states and the District of Columbia have laws regulating acupuncture practice, and most states require certification from the National Certification Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine. For more information, see NCCIH’s webpage on the credentials and licensing of complementary health practitioners.
- If you are pregnant or nursing or are thinking of using TCM to treat a child, be especially sure to consult your (or the child’s) health care provider.
- Tell all your health care providers about any complementary or integrative health approaches you use. Give them a full picture of what you do to manage your health. This will help ensure coordinated and safe care.
Eastern Exposure: How Traditional Chinese Medicine Can Keep You Healthy
Traditional Chinese medicine, with its talk of energy pathways and use of plants and roots to heal all manner of illness, has—to a Westerner used to checkups and prescriptions—an air of magical thinking. But major medical centers in the U.S. and Europe are realizing what they’re missing.
Drug researchers are combing ancient texts of traditional Chinese medicine, or TCM, seeking cures for diseases; it’s netted breakthroughs, such as the chemotherapy drug Taxol and the antimalarial treatment artemisinin.
Physicians wanting to offer patients better preventative care are incorporating TCM and calling their practices integrative or complementary medicine, which describes Eastern practices augmenting Western know-how.
In Eastern medicine, even the role of doctors is different. Here, you go to the doctor when you become ill.
“Traditionally, in Chinese medicine, you saw the doctor when you were well, and it was his job to keep you well,” says Shari Auth, a certified doctor of acupuncture and Chinese medicine.
Practitioners like Auth are taking TCM from niche to the mainstream.
Her practice in New York City, Wthn, makes it as easy to pop in for acupuncture as it is to get a lunchtime trim.
Major medical institutions, including Duke and the Mayo Clinic, have established integrative medicine clinics that may prescribe both an antianxiety drug and a course of yoga.
One major thing that sets Eastern medicine apart is that it sees our bodies as connected with the universe.
Chi (or qi) describes the life force that flows through the body via energy pathways.
Blockages result in pain and illness, which can be relieved with bodywork.
In our bodies, as well as in the universe, there is yin and yang, two opposing forces, where yin is cool and yang is hot.
If you have inflammation, which is excess heat, fresh fruits and vegetables (yin foods) help restore balance. If you are cold, hot soup or spices (yang foods) do the trick.
Next year, the World Health Organization is set to recognize TCM alongside Western practices.
And insurance companies are starting to cover alternative practices, which will help make it accessible to more people.
Now, no one should be tossing their beta-blockers.
TCM detractors say there’s insufficient clinical evidence.
And China has been accused of poaching and torturing animals in the name of medicine—including tigers, rhinoceroses, pangolins, and bears.
You don’t need to subscribe to all of TCM, but it provides a useful way to think about health.
It’s not about being sick versus not sick.
It’s about creating a well-being model, says Justin Laube, M.D., at UCLA’s Center for East-West Medicine. “We all have the ability to prevent and self-heal,” he says.
“We need guides.”
Start to view your health holistically and pay attention to all facets: sleep, diet, activity, social connections, mental health—even finding purpose and joy. It’s a lifelong task. “Tending to your health is like tending to a garden,” Laube says.
“You plant seeds, water them, weed out the bad.
By the time you’re older, you’ve got a flourishing, resilient garden.”
Bodywork
TCM regards bodywork as a tool for breaking up energy blockages.
Stateside, it’s used on athletes, chronic pain sufferers, and those with mental health issues.
Even the military is starting to promote medical acupuncture, including training medics who can treat soldiers in the field for physical pain and trauma.
Here are a few bodywork practices.
Acupuncture
We all have that friend who swears by it.
Might be time to give it a try.
This is the poster child of TCM.
Needles are placed in the body to facilitate the flow of chi.
Until recently, it’s had a niche vibe in the U.S.
But the number of people doing acupuncture nearly doubled from 2012 to 2017 and continues to rise, according to a survey from the National Center for Health Statistics.
What is it used for?
Many try it for a specific ailment— sports injury, bad back, chemo side effects, migraines—or for general well-being, pain relief, energy, and stress reduction.
It’s even being employed in heroin-addiction programs, including Penn North Recovery in West Baltimore.
Does it hurt?
Not really.
The needles used are thin—40 of them could fit inside a hypodermic needle.
You may feel a little discomfort at some points.
If you’re needle-averse, remind yourself these are for healing, not pain; some points are even soothing
Does it work?
Studies say yes.
A major review from the University of York in the U.K. shows people who receive acupuncture for chronic pain along with standard medical care have significantly better outcomes.
Some healing is credited to the interaction itself.
The practitioner asks about your well-being, giving you space to discuss what is bothering you.
And studies show that touch releases oxytocin, a feel-good chemical, which lowers cortisol to reduce stress.
After the needles are placed, you lie quietly and may meditate, which is good for your head.
But skip the pre-acupuncture java; an animal study in Scientific Reports suggests caffeine may lower sensitivity to treatment and inhibit pain relief.
Cupping
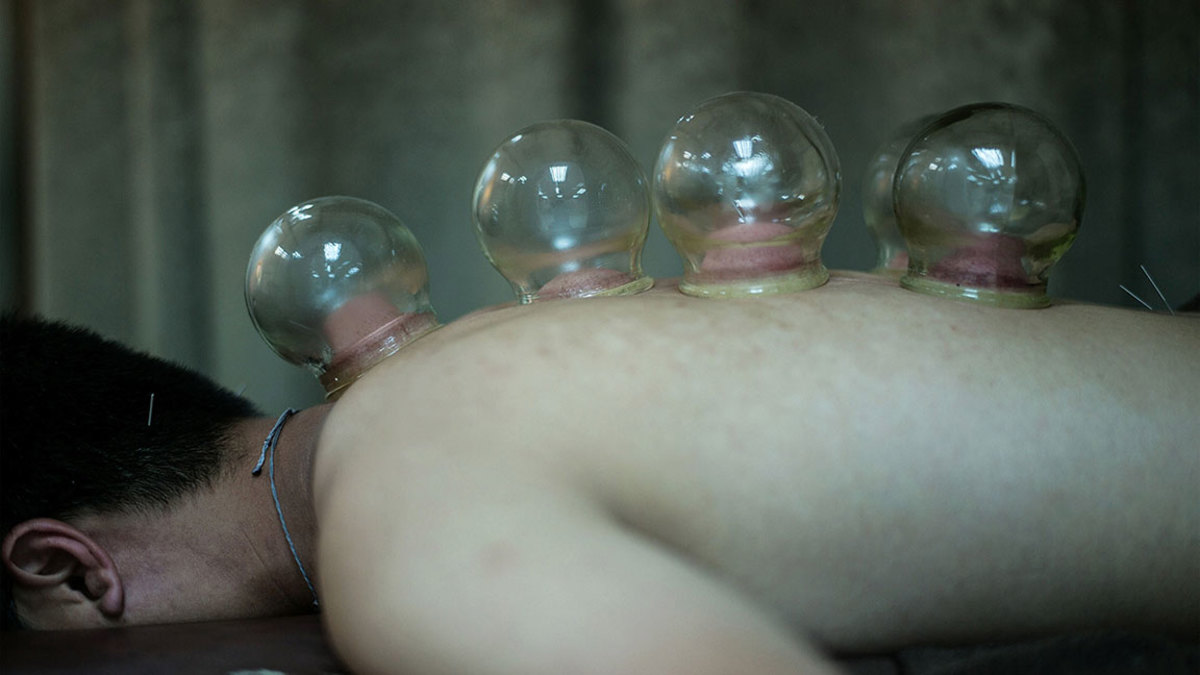 The preferred recovery method for top-of-their-game athletes
is the opposite of a massage. Michael Phelps introduced many of us to cupping when he showed up to the Summer Olympics in Rio with purple circles on his shoulder. Cups made of plastic or glass are
applied along the back, shoulders, chest, or legs. The air is removed to create a suction. The practitioner moves the cups around to increase circulation, relieve muscle tension, and accelerate
muscle recovery. The sensation can be intense on sensitive areas, so using a smaller cup or lowering the suction helps. It’s often done in the same session as acupuncture.
The preferred recovery method for top-of-their-game athletes
is the opposite of a massage. Michael Phelps introduced many of us to cupping when he showed up to the Summer Olympics in Rio with purple circles on his shoulder. Cups made of plastic or glass are
applied along the back, shoulders, chest, or legs. The air is removed to create a suction. The practitioner moves the cups around to increase circulation, relieve muscle tension, and accelerate
muscle recovery. The sensation can be intense on sensitive areas, so using a smaller cup or lowering the suction helps. It’s often done in the same session as acupuncture.Gua Sha
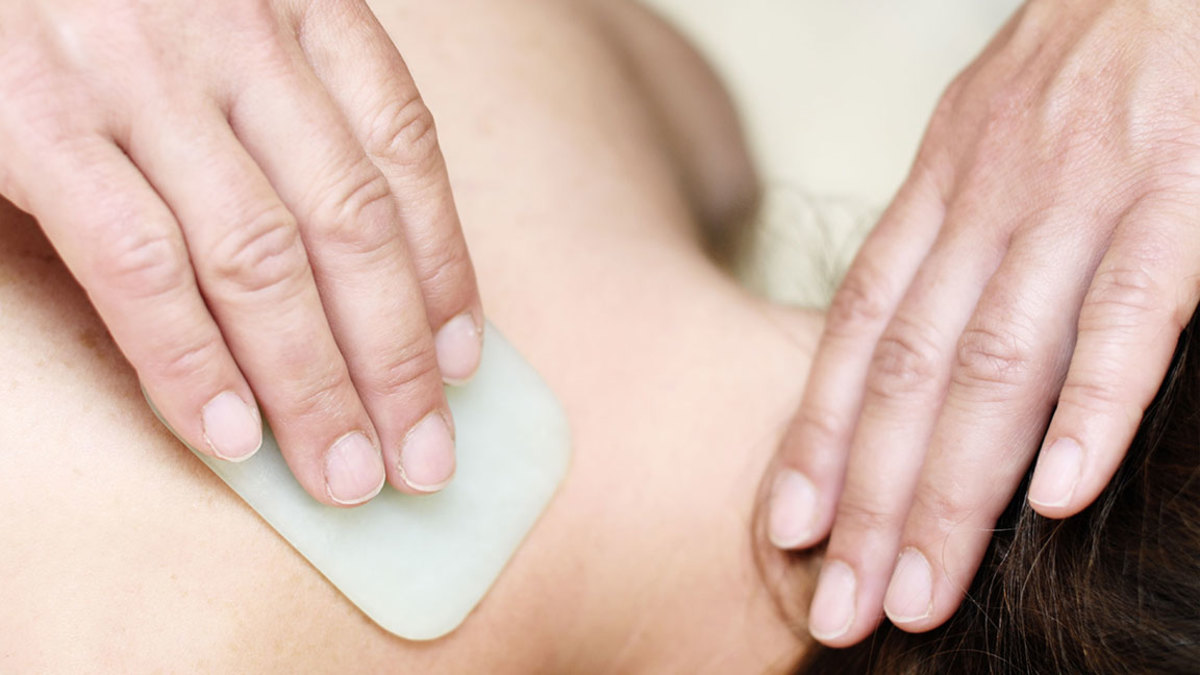 It’s like scraping away old paint—except it’s on your skin.
This form of bodywork involves scraping the skin, the same way you’d smooth air bubbles out of wallpaper. Traditionally it’s done with spoons, but modern practitioners use small wedges, often made
out of quartz. Like cupping, the motion may increase blood flow, release knots in muscles, and relieve soreness. If it’s done vigorously, you may be left with purple “stripes” the next day, but they
aren’t painful.
It’s like scraping away old paint—except it’s on your skin.
This form of bodywork involves scraping the skin, the same way you’d smooth air bubbles out of wallpaper. Traditionally it’s done with spoons, but modern practitioners use small wedges, often made
out of quartz. Like cupping, the motion may increase blood flow, release knots in muscles, and relieve soreness. If it’s done vigorously, you may be left with purple “stripes” the next day, but they
aren’t painful.Electronic Acupuncture Pen Meridian Energy Pen Pain Relief Electric Massage Pen
People also ask: (Google)
An acupuncture pen acts as a hybrid device that combines acupressure and acupuncture.
Unlike traditional acupuncture treatment, acupuncture pens don't contain needles.
Instead, it uses electrical impulses to stimulate acupressure points
It contains piezoelectric crystals that generate a charge when the button on top of the pen is pressed. The manufacturers claim that when the pen is used on a painful area, the electric charge stimulates a nerve pathway, which sends a "call to help" message to the brain.